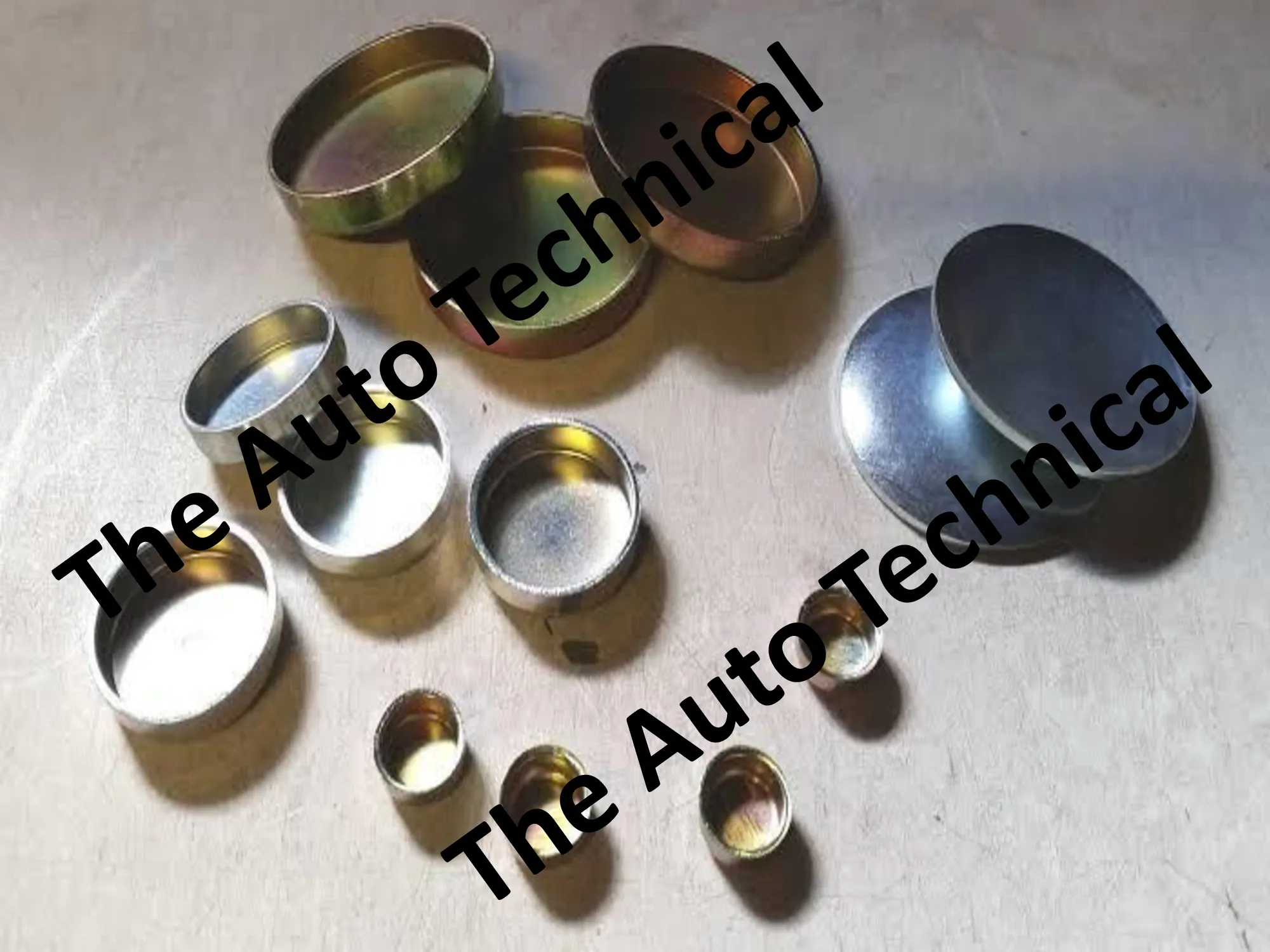
What is the Engine Core Plug
#mcq #quizquestion
#automotivequestions #automotivequizquestions #automotivetechnology #automobileengineering #automobiletechnology
Engine Core Plugs: Unsung Heroes of the Motor World
Engines are intricate pieces of machinery that power various forms of transportation, from cars and trucks to aircraft and boats. Within an engine, there are numerous components working in harmony to ensure it functions optimally.
One such often overlooked yet critical component is the engine core plug. In this article, we'll explore what an engine core plug is, the different types, their essential functions, the requirements they must meet, and conclude with their significance in the world of engines.
What is the Engine Core Plug?
An engine core plug, often referred to as a freeze plug or welch plug, is a small, seemingly insignificant component that plays a vital role in the overall functioning of an engine.
These plugs are typically made of metal, commonly steel, and are designed to seal or block off various openings or cavities in the engine block and cylinder head.
The term "freeze plug" is derived from their historical use to prevent engine damage caused by freezing water within the engine during cold temperatures.
Types of Engine Core Plugs
Engine core plugs come in several different types, each serving specific purposes within the engine. The main types of engine core plugs include:
1. Cup Type Plugs:
Cup-type core plugs are among the most common. They are concave in shape and fit into recessed holes in the engine block. These plugs are typically held in place by their tight fit and can be challenging to remove without the proper tools.
2. Disc Type Plugs:
Disc-type core plugs are flat, circular plugs that seal holes by sitting flush with the surface. They are secured in place with bolts and are easier to remove and replace compared to cup-type plugs.
3. Welch Plugs:
Welch plugs are similar to cup-type plugs but are often used to seal small coolant passages and other openings in the engine. They can be made of various materials, including rubber or steel.
4. Expansion Plugs:
Expansion plugs, also known as rubber plugs, are used in various engine applications. They are designed to expand when installed, effectively sealing the opening they are placed in.
Work of Engine Core Plug
The primary function of engine core plugs is to seal or block openings in the engine block and cylinder head. They serve several crucial purposes:
1. Coolant Passages:
Engine core plugs seal openings that allow coolant to circulate through the engine. This is vital for regulating the engine's operating temperature and preventing overheating.
2. Protection:
Core plugs protect the engine's internal components from debris, contaminants, and foreign materials that could enter and cause damage.
3. Preventing Freezing:
Historically, these plugs were used to prevent freezing of the engine's coolant during cold weather. If the coolant froze, it could expand and potentially crack the engine block. While modern engines use a mixture of water and antifreeze to prevent freezing, core plugs are still essential for their sealing properties.
4. Balancing Pressure:
Engine core plugs help balance the pressure inside the engine. They prevent the engine block from becoming distorted due to variations in temperature and pressure.
Requirements of Engine Core Plug
Engine core plugs must meet specific requirements to function effectively and maintain the engine's integrity. These requirements include:
1. Material Durability:
Core plugs must be made of materials that are resistant to corrosion and damage, as they are in direct contact with the engine's internal fluids.
2. Sealing Ability:
They should form a tight seal, preventing any leaks of coolant, oil, or other fluids.
3. Ease of Installation:
Core plugs should be relatively easy to install and replace when necessary. This ensures that maintenance or repairs can be conducted efficiently.
4. Resistance to Temperature Variations:
The materials used in core plugs must be able to withstand extreme temperature variations, as engines operate in conditions ranging from sub-zero cold to high heat.
5. Longevity:
Core plugs should have a long service life to reduce the frequency of replacements and maintenance.
Advantages of Engine Core Plugs:
1. Coolant Sealing:
One of the primary advantages of engine core plugs is that they effectively seal coolant passages in the engine block and cylinder head. This is crucial for maintaining the engine's operating temperature and preventing overheating. Without these plugs, coolant could leak out, leading to engine damage.
2. Protection from Debris:
Engine core plugs serve as protective barriers, preventing debris, contaminants, and foreign materials from entering the engine. This is particularly important in ensuring the longevity of the engine's internal components, such as the pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft.
3. Historical Freezing Prevention:
As the name "freeze plugs" suggests, they were originally designed to prevent engine damage caused by freezing coolant. While modern engines use antifreeze to prevent freezing, these plugs still play a role in sealing coolant passages and maintaining the overall integrity of the engine.
4. Balancing Pressure:
Engine core plugs help balance pressure within the engine. This is essential to prevent the engine block from distorting due to fluctuations in temperature and pressure. Properly balanced pressure ensures the engine's structural integrity.
5. Versatility:
There are different types of engine core plugs, each designed for specific applications. This versatility allows them to be used in various parts of the engine, providing customized solutions for sealing and protection.
Disadvantages of Engine Core Plugs:
1. Vulnerability to Corrosion:
Engine core plugs are typically made of metal, such as steel, which can be vulnerable to corrosion over time. If the plug corrodes or rusts, it can compromise its ability to seal openings effectively, leading to coolant leaks or other issues.
2. Difficulty in Replacement:
In some cases, engine core plugs can be challenging to replace, especially if they are the cup-type plugs. Removing them without damaging the engine block can be a complex and time-consuming process, requiring specialized tools and expertise.
3. Potential for Failure:
Like any mechanical component, engine core plugs can fail, either due to manufacturing defects, material fatigue, or improper installation. A failing core plug can lead to coolant leaks, which, if not addressed promptly, can cause engine overheating and damage.
4. Limited Lifespan:
Engine core plugs have a finite lifespan, and they may need replacement during the engine's lifetime. This can add to maintenance costs and, in some cases, require disassembling a part of the engine to access and replace the plugs.
5. Maintenance Requirement:
As engine core plugs age and may develop issues, they require periodic inspection and potential replacement. Neglecting this maintenance can lead to more extensive and costly engine problems.
How to Choose Correct Engine Core Plug:
Choosing the correct engine core plug is essential for maintaining the integrity and performance of your engine. These plugs come in various types and sizes to suit different engine designs and requirements. Here are some steps to help you select the right engine core plug:
1. Identify Your Engine Model and Year:
The first step is to identify the specific make, model, and year of your engine. Different engines may have different core plug requirements, so this information is crucial.
2. Determine the Core Plug Type:
There are various types of engine core plugs, including cup-type, disc-type, welch plugs, and expansion plugs. The type you need depends on the application and the engine design. Refer to your engine's specifications or consult with the manufacturer or a trusted mechanic to determine the correct type.
3. Consider Material:
Engine core plugs are typically made of steel, but there are variations, including brass and rubber. The material may affect the plug's durability and resistance to corrosion. For most applications, steel core plugs are suitable, but if you are dealing with specialized engine requirements, consult an expert to choose the appropriate material.
4. Check the Size and Diameter:
Engine core plugs come in various sizes and diameters. It's crucial to measure the opening that needs to be sealed accurately. Use a caliper or ruler to measure the inner diameter of the opening. Be precise, as even a small discrepancy can lead to an ill-fitting plug.
5. Verify the Shape and Design:
The shape and design of the plug should match the opening in the engine block or cylinder head. For example, cup-type plugs are concave and fit into recessed holes, while disc-type plugs are flat and seal openings by sitting flush with the surface. Ensure that the design corresponds to the engine's configuration.
6. Consider Special Applications:
In some cases, you may have unique engine requirements, such as high-performance or racing engines that require specialized core plugs. Consult with experts or manufacturers who cater to these specific applications for guidance.
7. Examine the Conditions:
Consider the conditions under which the engine operates. If it's in a harsh environment, exposed to extreme temperatures, or subjected to unusual stress, you may need core plugs made from more durable materials or with added features like corrosion-resistant coatings.
8. Consult with a Mechanic or Expert:
If you are unsure about the specific core plug requirements for your engine, it's always a good idea to consult with a qualified mechanic or an expert in engine components. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on your engine's unique needs.
9. Quality and Brand Reputation:
Choose high-quality core plugs from reputable brands or manufacturers. Quality matters as it can affect the plug's longevity and performance. A reliable core plug is more likely to provide a tight and durable seal.
10. Consider OEM Parts:
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) core plugs are designed to meet the specifications of your engine. Using OEM parts can provide peace of mind that the core plug will fit and function as intended.
11. Maintenance Schedule:
If you are replacing core plugs as part of a maintenance schedule, be sure to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for when and how often to change these components.
12. Installation Expertise:
If you are not experienced with engine maintenance, consider having a professional mechanic or technician install the core plug for you. Proper installation is crucial for the plug's effectiveness.
How to Remove or Fit the Engine Core Plug:
Removing or fitting an engine core plug, also known as a freeze plug or welch plug, can be a straightforward task or a more involved process depending on the type of plug and its location.
Below, I'll provide a general guide on how to remove and fit core plugs, but please keep in mind that specific engine configurations and core plug types may require slight variations in the process.
1. Removing an Engine Core Plug:
(a) Tools and Materials Needed:
- Screwdriver or punch
- Hammer
- Chisel or seal puller (if necessary)
- Replacement core plug (if needed)
- Gasket sealant (if needed)
(b) Steps:
Safety First:
Make sure the engine is completely cool and, if necessary, drained of coolant. Always wear safety goggles and gloves when working on the engine.
Identify the Core Plug:
Locate the core plug you need to remove. Core plugs are typically positioned in the engine block and cylinder head, so access may require removing other engine components or covers.
Assess the Plug Type:
Determine the type of core plug you're dealing with (cup-type, disc-type, etc.) as this will influence the removal process.
Use a Screwdriver or Punch:
For cup-type core plugs, insert a screwdriver or punch into the center of the plug, near the edge. With a hammer, tap the screwdriver or punch gently to create a slight dent or hole in the plug.
Pry the Plug:
Once you've created a dent or hole, you can use a screwdriver or chisel to carefully pry the core plug out of its seat. Start at the dent or hole and work your way around the edge. Be patient and cautious to avoid damaging the engine block.
Clean the Seating Surface:
After removing the core plug, clean the seating surface thoroughly. Remove any rust, debris, or old gasket material to ensure a proper seal when fitting the new plug.
Inspect for Damage:
Examine the core plug cavity for any signs of damage or corrosion. If the cavity is compromised, it may need repair or further attention before fitting the new plug.
2. Fitting a New Engine Core Plug:
(a) Tools and Materials Needed:
- Replacement core plug
- Hammer
- Sealant (gasket sealant or thread sealant, if needed)
(b) Steps:
Select the Right Replacement Plug:
Make sure the replacement core plug is the correct type, size, and material for your engine. Double-check that it matches the plug you removed.
Apply Sealant (if necessary):
Depending on your engine's specifications and recommendations, you may need to apply a thin layer of gasket sealant or thread sealant to the outer edge of the new core plug. This helps ensure a tight and leak-free seal.
Position the Plug:
Carefully position the new core plug into the cavity, aligning it correctly with the opening.
Use a Hammer:
Gently tap the center of the core plug with a hammer. Start with light taps and gradually increase the force until the plug is firmly seated. Be cautious not to overdo it, as excessive force could damage the plug or the engine block.
Inspect for Leaks:
Once the new core plug is in place, inspect for any leaks. Afterward, refill the coolant system (if applicable) and monitor it for leaks during the initial startup and running of the engine.
Conclusion
Engine core plugs are often overshadowed by more prominent engine components, but their role in maintaining engine integrity is indispensable.
They come in various types, each serving a specific purpose, from sealing coolant passages to protecting the engine from freezing. These plugs must meet essential requirements to fulfill their duties effectively.
The next time you start your vehicle or embark on a journey by plane or boat, spare a thought for these unsung heroes of the motor world – the engine core plugs – silently ensuring the engine's smooth operation and longevity.
In summary, while engine core plugs may seem unremarkable, they are crucial to the reliability and performance of any engine. Understanding their types, functions, and requirements is essential for ensuring the smooth operation of vehicles and machinery powered by internal combustion engines.















.webp)

0 تعليقات